Beauty and a youthful appearance are very important in Southern California. You most likely try to achieve or maintain both beauty and youthfulness with exercise, a healthy diet and skin care regimen with daily sunscreen application. Since glowing skin is a main component of appearance, you may tan at the beach or in tanning beds. However, overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) light also cause sun damage, premature aging and may lead to skin cancer.
SUN DAMAGE AND AGE SPOTS
Age spots from sun damage are typically harmless but are cosmetic imperfections that will require treatment from a dermatologist. They may be lightened with bleaching solutions or minimized or eradicated with laser treatment. Yet prevention is the best way to limit their appearance. Also read Fact & Fiction on Sun Damage, Part 1 for more tips.
Sunscreen
When you are in direct sunlight, swimming or sweating, sunscreen should be applied every two hours. SPF 30 or higher should be applied daily on your face and the entire body, even under clothing. This is especially important when you are in the sun for an extended period.
Limiting exposure
Limit your sun exposure outside. This includes wearing and reapplying sunscreen every two hours. Additionally, you should wear sunglasses with a high level of protection, a wide-brimmed hat, baseball cap or sun visor, and protective, sun-protective clothing.
UV Protection Films
If you spend numerous hours each weak in your car as part of your daily commute, applying UVA film to your car windows. Unintentionally exposed to both UVA and UVB light can lead to sun damage
Laser Removal
Laser treatments work two-fold by destroying melanocytes and breaking up melanin. Two types of lasers accomplish this with light heat, Fraxel and Spectra.
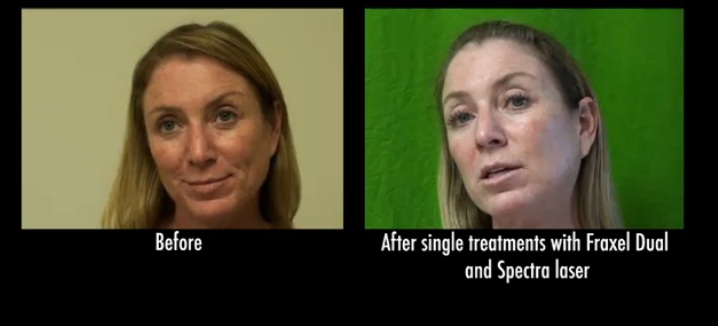
Patient with age spots and other forms of sun damage before and after using laser treatments, including Fraxel Dual and Spectra*
FACT VERSUS FICTION ON SUN DAMAGE
Base tans prevent sunburns: FALSE
Whenever you tan or get sunburned, it signifies DNA damage. Fairer skin tones are more prone to sunburns and sun damage than darker skin tones since darker skin tones doesn’t burn quite as easily. More pigment is found in darker skin tones, which provides more melanin and more natural protection. However, a tan or sunburn on any skin tone is a symptom of your body’s attempt to repair your skin’s cellular damage.
You should wear sunscreen under your clothes: TRUE
Most clothing provides very little sun protection. For instance, a white T-shirt provides only SPF 7; if wet, its SPF 3. While darker and thicker the clothing provides more protection from sun damage, it’s also hotter. Therefore, if you place to be outside for a while, apply sunscreen on your entire body before getting dressed.
SPF 30 is twice as strong as SPF 15: FALSE
SPF numbers are misleading and currently undergoing a new rating system to address these misconceptions. SPF 15 blocks 93 percent of UVB rays but SPF 30 provides only 3 percent more protection with blocking 97 percent. As the SPF numbers go up, the UVB ray blockage in minimal. SPF 50 provides 98 percent protection and SPF 100 provides 99 percent protection. One of the most effective ways for sunscreen to continuously work is to simply reapply it every two hours.
Dr. Sanusi Umar is a board certified Los Angeles dermatologist and surgical dermatologist who is an expert in skin rejuvenation. His FineTouch Dermatology clinic can assist you with an array of skin and sun damage needs.
